ROS2-Z02-ROS2工具:坐标变换(EXEC2)乌龟护航案例实战
简介
本章节主要介绍如何实现 “乌龟护航” 案例。里面的大部分代码会沿用上一章节,即ROS2-Z01-ROS2工具:坐标变换(EXEC1)乌龟跟随案例实战内的相关代码内容。因此建议先尝试实现上一章节的效果,再来进行本章节的实战。
案例需求&分析
需求: 基于上一章节要求编写程序实现,以 turtlesim_node 节点的原生乌龟(turtle1)为几何中心,生成多只新的乌龟(以三只为例,即turtle2、turtle3、turtle4)。要求在 turtle1 无论是静止或是被键盘控制运动时,turtle2 都会以 turtle1 的几何中心为目标并以某种队形对其进行护航。
分析: 上一章节中,“乌龟跟随” 案例的核心是如何确定 turtle1 相对 turtle2 的位置,只要该位置确定就可以把其作为目标点并控制 turtle2 向其运动。而在这一章节中,案例的核心就变成了如何确定原生乌龟 turtle1 所制定的各个点位相对于其他 turtle 的位置。这些相对位置的确定同样可以通过坐标变换实现,其中:
- 队列的各个点位相对于原生乌龟
turtle1的坐标系静止,就可以通过静态广播的方式发布这些 静态坐标点 相对于原生乌龟的位置关系。 - 而针对乌龟,是先分别广播各个乌龟 相对于
world的坐标系关系,然后再通过监听坐标系关系进一步获取 静态坐标点 相对于turtle的坐标系关系。
这样就可以在换算出坐标关系后,通过计算、发布相应的速度指令控制多个乌龟的护航了。
流程简介
案例中关于“生成新乌龟”、“乌龟坐标系变换广播与监听”都已经实现,因此这里仅需编写launch文件组织节点即可。主要步骤如下:
- 编写
launch文件集成相关节点; - 编译;
- 执行。
案例我们依然会采用 C++ 和 Python 分别实现,二者都遵循上述实现流程。
准备工作
参考上一章节,即ROS2-Z01-ROS2工具:坐标变换(EXEC1)乌龟跟随案例实战。特别推荐先实现该实战再来做本实战。
案例实现
1. 编写 launch 文件集成相关节点
我们可以先实现 一只 乌龟的护航,要求其最终位置在原生乌龟附近特定位置:
功能包 cpp05_exercise 的 launch 目录下,新建 python 文件 escort.launch.py,并编辑文件,输入如下内容:
from launch import LaunchDescription
from launch_ros.actions import Node
# 参数声明与获取-----------------
from launch.actions import DeclareLaunchArgument
from launch.substitutions import LaunchConfiguration
"""
需求:实现乌龟护航案例
-----------------------------
先实现一只乌龟护航,要求其最终位置在原生乌龟附近特定位置
思路:
1. 发布目标点相对于原生乌龟的坐标变换
2. 监听 该乌龟 与目标点相对于坐标系的关系
实现流程:
1. 抽取参数;
2. 创建 turtlesim_node 节点,并生成新乌龟;
3. 发布坐标变换;
4. 监听坐标变换。
"""
def generate_launch_description():
# 1. 抽取参数;
escort_back = DeclareLaunchArgument(name="turtle_back", default_value="turtle_back")
# 2. 创建 turtlesim_node 节点,并生成新乌龟E1;
master = Node(package="turtlesim", executable="turtlesim_node")
spawn_back = Node(package="cpp05_exercise", executable="exec01_spawn", name="spawn_back", parameters=[{
"x": 2.0,
"y": 5.0,
"turtle_name": LaunchConfiguration("turtle_back")
}])
# 3. 发布坐标变换;
# 3.1 乌龟坐标系广播
turtle1_world = Node(package="cpp05_exercise", executable="exec02_tf_broadcaster", name="turtle1_world")
back_world = Node(package="cpp05_exercise", executable="exec02_tf_broadcaster", name="back_world", parameters=[{
"turtle": LaunchConfiguration("turtle_back")
}])
# 3.2 静态坐标点广播
escort_point_back = Node(package="tf2_ros", executable="static_transform_publisher", name="escort_point_back", arguments=["--frame-id", "turtle1", "--child-frame-id", "escort_point_back", "--x", "-1.5"])
# 4. 监听坐标变换。
back_ep_back = Node(package="cpp05_exercise", executable="exec03_tf_listener", name="back_ep_back", parameters=[{
"father_frame": LaunchConfiguration("turtle_back"),
"child_frame": "escort_point_back"
}])
return LaunchDescription([
escort_back,
master,
spawn_back,
turtle1_world,
back_world,
escort_point_back,
back_ep_back
])之后就可以通过修改上述代码实现其他乌龟的护航了:
from launch import LaunchDescription
from launch_ros.actions import Node
# 参数声明与获取-----------------
from launch.actions import DeclareLaunchArgument
from launch.substitutions import LaunchConfiguration
"""
需求:实现乌龟护航案例
思路:
1. 发布目标点相对于原生乌龟的坐标变换
2. 监听 新乌龟 与目标点相对于坐标系的关系
实现流程:
1. 抽取参数;
2. 创建 turtlesim_node 节点,并生成新乌龟;
3. 发布坐标变换;
4. 监听坐标变换。
"""
def generate_launch_description():
# 1. 抽取参数;
escort_back = DeclareLaunchArgument(name="turtle_back", default_value="turtle_back")
escort_left = DeclareLaunchArgument(name="turtle_left", default_value="turtle_left")
escort_right = DeclareLaunchArgument(name="turtle_right", default_value="turtle_right")
# 2. 创建 turtlesim_node 节点,并生成新乌龟;
master = Node(package="turtlesim", executable="turtlesim_node")
spawn_back = Node(package="cpp05_exercise", executable="exec01_spawn", name="spawn_back", parameters=[{
"x": 2.0,
"y": 5.0,
"turtle_name": LaunchConfiguration("turtle_back")
}])
spawn_left = Node(package="cpp05_exercise", executable="exec01_spawn", name="spawn_left", parameters=[{
"x": 4.0,
"y": 7.0,
"turtle_name": LaunchConfiguration("turtle_left")
}])
spawn_right = Node(package="cpp05_exercise", executable="exec01_spawn", name="spawn_right", parameters=[{
"x": 4.0,
"y": 3.0,
"turtle_name": LaunchConfiguration("turtle_right")
}])
# 3. 发布坐标变换;
# 3.1 乌龟坐标系广播
turtle1_world = Node(package="cpp05_exercise", executable="exec02_tf_broadcaster", name="turtle1_world")
back_world = Node(package="cpp05_exercise", executable="exec02_tf_broadcaster", name="back_world", parameters=[{
"turtle": LaunchConfiguration("turtle_back")
}])
left_world = Node(package="cpp05_exercise", executable="exec02_tf_broadcaster", name="left_world", parameters=[{
"turtle": LaunchConfiguration("turtle_left")
}])
right_world = Node(package="cpp05_exercise", executable="exec02_tf_broadcaster", name="right_world", parameters=[{
"turtle": LaunchConfiguration("turtle_right")
}])
# 3.2 静态坐标点广播
escort_point_back = Node(package="tf2_ros", executable="static_transform_publisher", name="escort_point_back", arguments=["--frame-id", "turtle1", "--child-frame-id", "escort_point_back", "--x", "-1.5"])
escort_point_left = Node(package="tf2_ros", executable="static_transform_publisher", name="escort_point_left", arguments=["--frame-id", "turtle1", "--child-frame-id", "escort_point_left", "--y", "1.5"])
escort_point_right = Node(package="tf2_ros", executable="static_transform_publisher", name="escort_point_right", arguments=["--frame-id", "turtle1", "--child-frame-id", "escort_point_right", "--y", "-1.5"])
# 4. 监听坐标变换。
back_ep_back = Node(package="cpp05_exercise", executable="exec03_tf_listener", name="back_ep_back", parameters=[{
"father_frame": LaunchConfiguration("turtle_back"),
"child_frame": "escort_point_back"
}])
left_ep_left = Node(package="cpp05_exercise", executable="exec03_tf_listener", name="left_ep_left", parameters=[{
"father_frame": LaunchConfiguration("turtle_left"),
"child_frame": "escort_point_left"
}])
right_ep_right = Node(package="cpp05_exercise", executable="exec03_tf_listener", name="right_ep_right", parameters=[{
"father_frame": LaunchConfiguration("turtle_right"),
"child_frame": "escort_point_right"
}])
return LaunchDescription([
escort_back,
escort_left,
escort_right,
master,
spawn_back,
spawn_left,
spawn_right,
turtle1_world,
back_world,
left_world,
right_world,
escort_point_back,
escort_point_left,
escort_point_right,
back_ep_back,
left_ep_left,
right_ep_right
])功能包 py05_exercise 的 launch 目录下,新建 python 文件 escort.launch.xml,并编辑文件,输入如下内容:
<launch>
<arg name="turtle_back" default="turtle_back"/>
<arg name="turtle_left" default="turtle_left"/>
<arg name="turtle_right" default="turtle_right"/>
<!-- 1. turtlesim_node -->
<node pkg="turtlesim" exec="turtlesim_node"/>
<!-- 2. 自定义的乌龟生成节点 -->
<node pkg="py05_exercise" exec="exec01_spawn_py" name="spawn_back">
<param name="x" value="2.0" />
<param name="y" value="5.0" />
<!-- <param name="theta" value="3.0" /> -->
<param name="turtle_name" value="$(var turtle_back)" />
</node>
<node pkg="py05_exercise" exec="exec01_spawn_py" name="spawn_left">
<param name="x" value="4.0" />
<param name="y" value="7.0" />
<!-- <param name="theta" value="3.0" /> -->
<param name="turtle_name" value="$(var turtle_left)" />
</node>
<node pkg="py05_exercise" exec="exec01_spawn_py" name="spawn_right">
<param name="x" value="4.0" />
<param name="y" value="3.0" />
<!-- <param name="theta" value="3.0" /> -->
<param name="turtle_name" value="$(var turtle_right)" />
</node>
<!-- 3.1 广播乌龟的坐标变换 -->
<node pkg="py05_exercise" exec="exec02_tf_broadcaster_py" name="turtle1_world"/>
<node pkg="py05_exercise" exec="exec02_tf_broadcaster_py" name="back_world">
<param name="turtle" value="$(var turtle_back)"/>
</node>
<node pkg="py05_exercise" exec="exec02_tf_broadcaster_py" name="left_world">
<param name="turtle" value="$(var turtle_left)"/>
</node>
<node pkg="py05_exercise" exec="exec02_tf_broadcaster_py" name="right_world">
<param name="turtle" value="$(var turtle_right)"/>
</node>
<!-- 3.2 广播坐标点的坐标变换 -->
<node pkg="tf2_ros" exec="static_transform_publisher" name="escort_point_back" args="--frame-id turtle1 --child-frame-id escort_point_back --x -1.5"/>
<node pkg="tf2_ros" exec="static_transform_publisher" name="escort_point_left" args="--frame-id turtle1 --child-frame-id escort_point_left --y 1.5"/>
<node pkg="tf2_ros" exec="static_transform_publisher" name="escort_point_right" args="--frame-id turtle1 --child-frame-id escort_point_right --y -1.5"/>
<!-- 4. 创建监听节点 -->
<node pkg="py05_exercise" exec="exec03_tf_listener_py" name="back_ep_back">
<param name="father_frame" value="$(var turtle_back)"/>
<param name="child_frame" value="escort_point_back"/>
</node>
<node pkg="py05_exercise" exec="exec03_tf_listener_py" name="left_ep_left">
<param name="father_frame" value="$(var turtle_left)"/>
<param name="child_frame" value="escort_point_left"/>
</node>
<node pkg="py05_exercise" exec="exec03_tf_listener_py" name="right_ep_right">
<param name="father_frame" value="$(var turtle_right)"/>
<param name="child_frame" value="escort_point_right"/>
</node>
</launch>2. 编译
colcon build --packages-select cpp05_exercisecolcon build --packages-select py05_exercise3. 执行
当前工作空间下启动终端,输入如下命令运行 launch 文件:
. install/setup.bash
ros2 launch cpp05_exercise escort.launch.py. install/setup.bash
ros2 launch py05_exercise escort.launch.xml再另外新建一终端,启动 turtlesim 键盘控制节点:
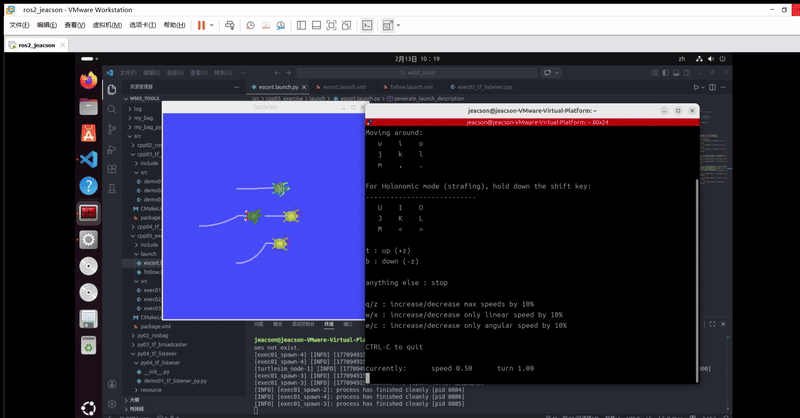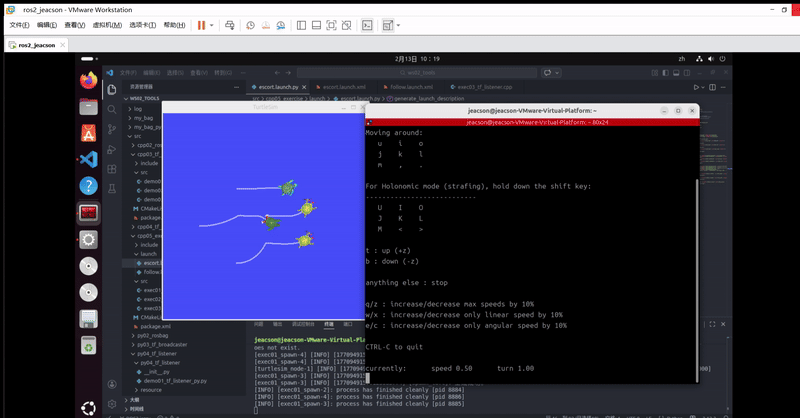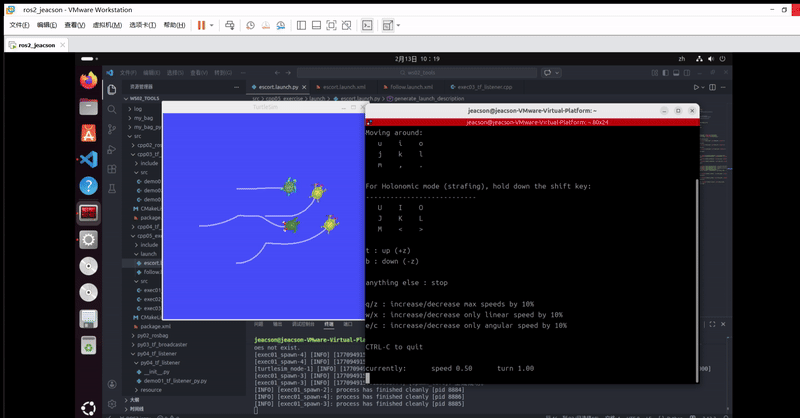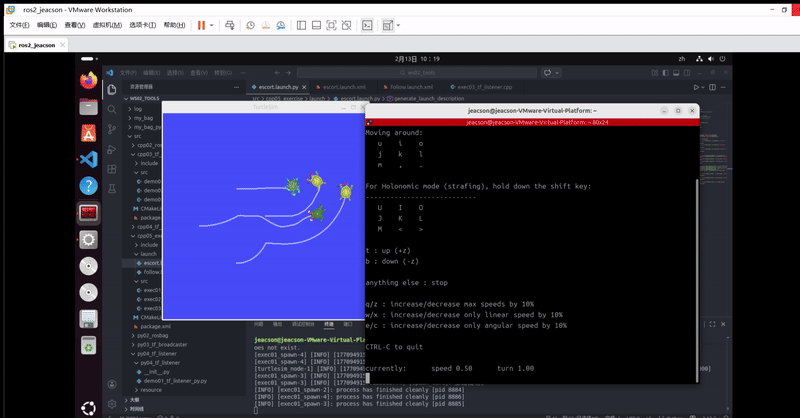
ros2 run turtlesim turtle_teleop_key该终端下可以通过键盘控制 原生乌龟 运动,并且 其他三只乌龟 会跟随 原生乌龟 运动。最终的运行结果如下:
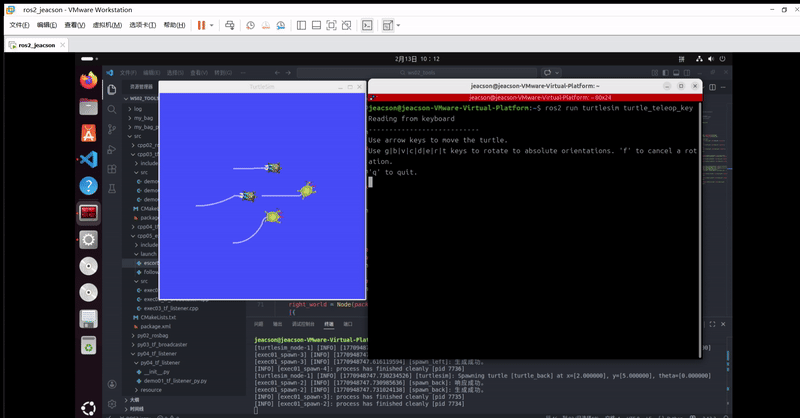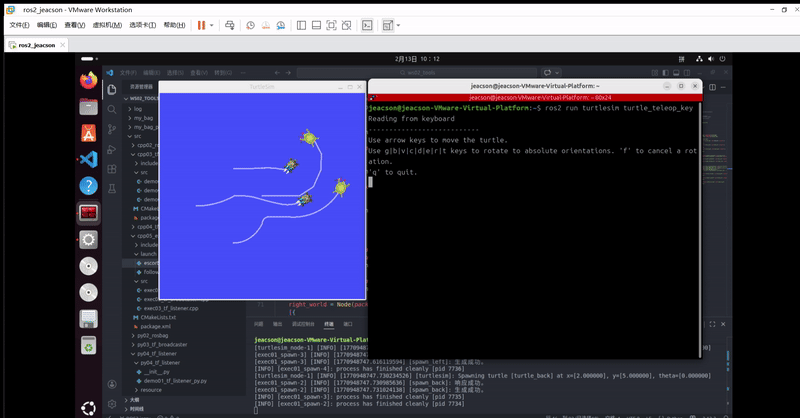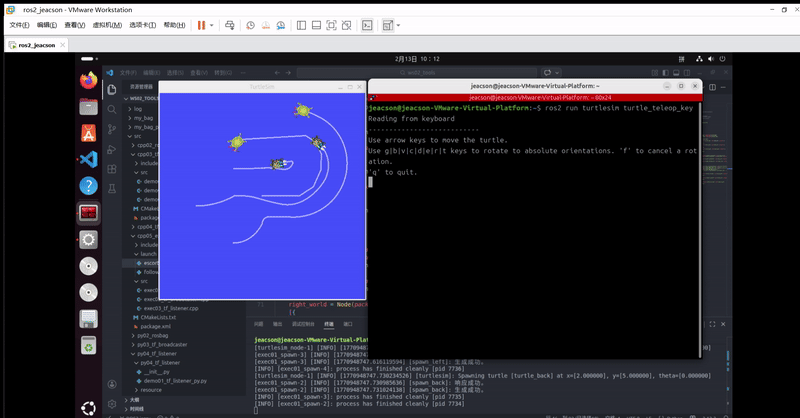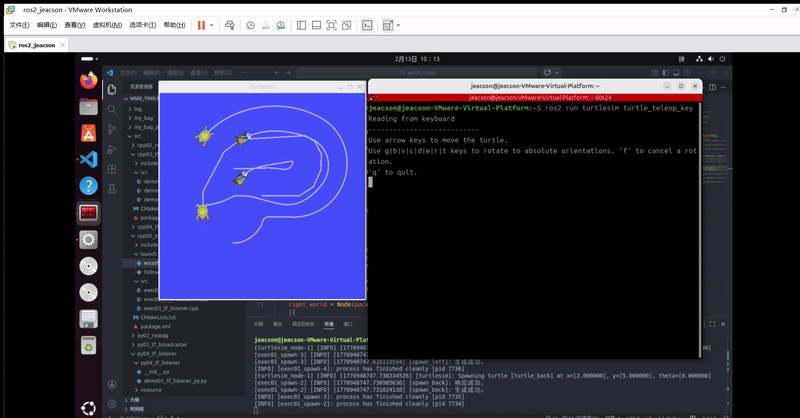
当然,你可能会发现:由于原生乌龟移动速度过快,另外三只跟随不上。
在此你可以使用另外一个控制节点:
ros2 run teleop_twist_keyboard teleop_twist_keyboard --ros-args --remap /cmd_vel:=/turtle1/cmd_vel运行结果如下: